How to know irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome
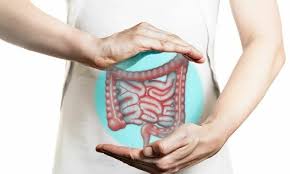
a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract (with no identifiable organic cause). It is the most common gastrointestinal diagnosis in North America, with a prevalence of 10%-15%. IBS presents most commonly in young women as chronic, crampy abdominal pain with alternating episodes of constipation and diarrhea. Passage of stool often relieves the pain.
It can also present with nonspecific symptoms such as gastroesophageal reflux, dysphagia, early satiety, and chest pain.
IBS is further subclassified as diarrhea—predominant, constipation—predominant, or mixed.
IBS was previously considered a diagnosis of exclusion. However, patients with IBS :: symptoms based on the ROME I criteria, no alarm features, and no family history of inflammatory bowel disease or colorectal cancer do not require extensive workup. Colonoscopy performed on IBS patients typically shows normal colonic mucosa.
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/irritable-bowel-syndrome



