Melasma
Unlocking the Secrets to Radiant Skin: A Comprehensive Guide to Treating Melasma Naturally and Effectively
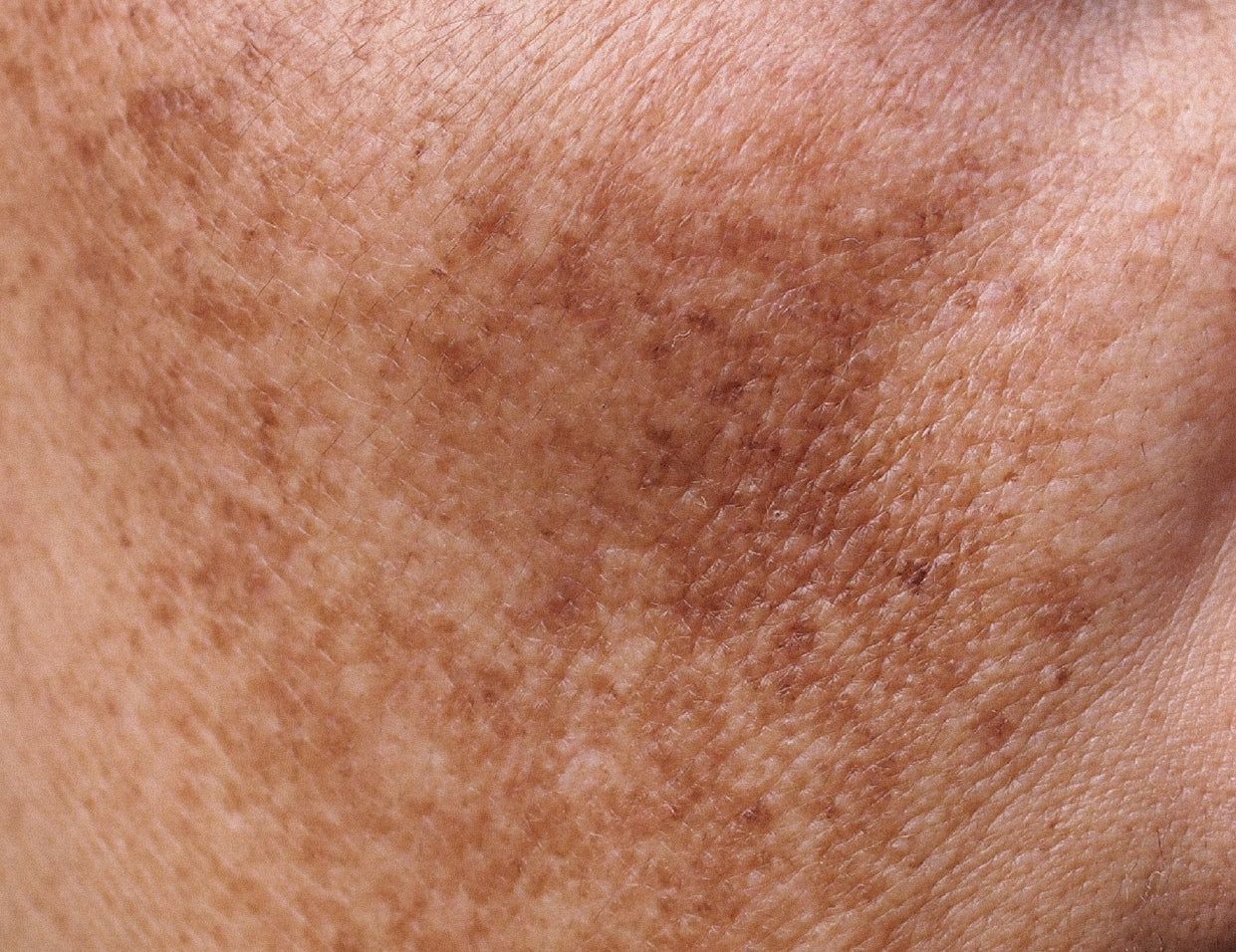
Melasma is a common skin problem caused by brown to gray-brown patches on the face. Most people get it on their cheeks, chin, nose bridge, forehead, and above the upper lip. It is more common in women than men. Pregnancy is a common cause of melasma. It also affects woman taking oral contraceptives and hormones.
Etiologic factors include genetic influences, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, pregnancy, hormonal therapies, cosmetics, phototoxic drugs, and antiseizure medications.
Melasma stimulates melanocytes by the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone, producing more melanin pigments when the skin is exposed to the sun
Sunlight Exposure
UV radiation can cause lipids peroxidation in cellular membranes, resulting in free radicals which could stimulate melanocytes to produce excess melanin.
- Sunscreens that block UV-B radiation (290-320 nm) do not block the longer wavelengths of UV-A and visible radiation (320-700 nm) which also stimulate melanocytes to produce melanin.
Hormonal Influences
Hormones may play a role in developing melasma in some individuals.
- The mask of pregnancy is known to occur in obstetric patients. The exact mechanism is unknown. Estrogen, progesterone, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone levels are normally increased during the third trimester of pregnancy and may be a factor.
- Patients with melasma who are nulliparous have no increased levels of estrogen or MSH but show elevated levels of estrogen receptors within the lesions. In addition, melasma with estrogen- and progesterone-containing oral contraceptive pills and diethylstilbestrol treatment for prostate cancer have been observed.
- A woman who is postmenopausal and given progesterone may develop melasma, while those who are given estrogen alone do not; this implicates progesterone as playing a primary role in the development of melasma.
Treatment
- Sunscreen
- Topical depigmenting agents :
-Hydroquinone:
Contraindications
- History of sensitivity or allergic reaction to hydroquinone or any ingredient in the formulation.
Warnings/Precautions
Warnings
Cosmetic Effects
May produce undesired cosmetic effects (e.g., excessive skin bleaching) if not used as directed. Clinician should be familiar with the use, adverse effects, precautions, and contraindications before prescribing or dispensing the drug.
Exposure to Sunlight or Ultraviolet Light
Exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light may cause repigmentation of bleached areas. [ref] Avoid unnecessary exposure to sunlight during and after therapy.
Sunscreen agents and/or protective clothing recommended if preparations which do not contain sunscreen are applied during the daytime. [ref] Preparations containing sunscreen may provide sufficient protection from sunlight.
After reduction of hyperpigmentation and during maintenance therapy, continue the use of sunscreen agents and/or protective clothing.
Sensitivity Reactions
Sulfite Sensitivity
Some formulations contain sulfites, which may cause allergic-type reactions (including anaphylaxis and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes) in certain susceptible individuals.
Other Sensitivity Reactions
Contact dermatitis reported. If contact dermatitis occurs, discontinue immediately and contact a clinician.
Major Toxicities
Rarely, ochronosis (gradual blue-black darkening of the skin) and colloid milium reported with chronic use (up to 8 years) of 5% hydroquinone cream. If affected skin changes to a blue-black color, discontinue immediately and contact a clinician.
General Precautions
Topical Use
For external use only. Not for topical application in the eyes, ears, or mouth; to cut, abraded, or sunburned skin; after shaving or using a depilatory agent; or over miliaria rubra (prickly heat).
Dermatologic Effects
Possible local skin irritation (e.g., burning, stinging, mild erythema). Dryness and fissuring of paranasal and infraorbital areas reported.
Use of Fixed Combinations
When hydroquinone is used in fixed combination with topical sunscreens (e.g., dioxybenzone, oxybenzone, and padimate), fluocinolone, or retinoids (e.g., tretinoin), consider the cautions, precautions, and contraindications associated with these agents.
Specific Populations
Pregnancy
Category C.
Lactation
Not known if topical hydroquinone is distributed into milk. [ref] Caution advised if topical hydroquinone is used.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of hydroquinone preparations not established in children <12 years of age.
Safety and efficacy of the fixed-combination hydroquinone, fluocinolone, and tretinoin cream not established in pediatric patients of any age.
-Rucinol:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17388924/