Clinical features of type 2 heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia
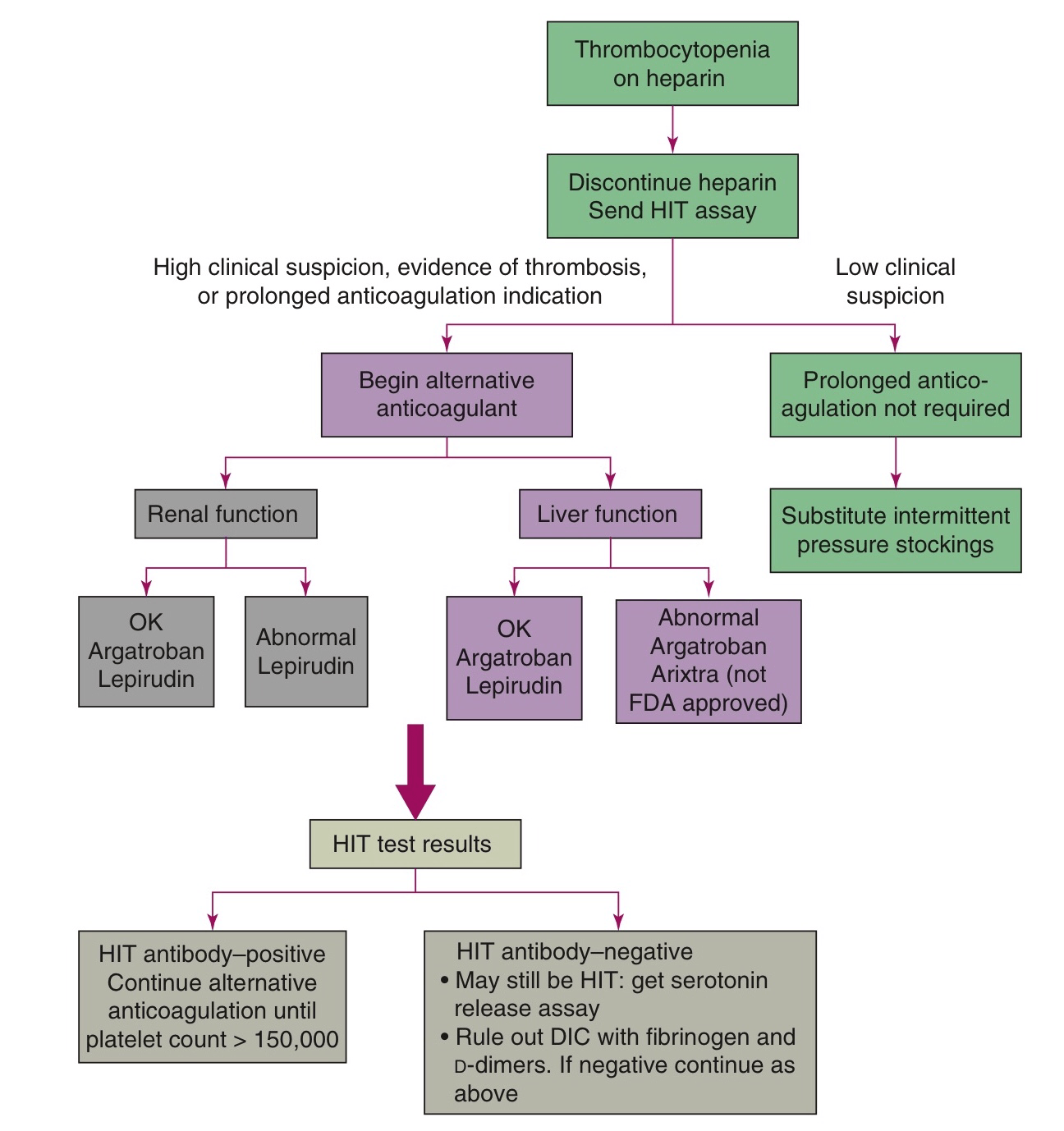
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a life—threatening complication of heparin therapy. Heparin induces a conformational change in a platelet surface protein (platelet factor 4), which exposes a neoantigen. In patients with HIT, HIT antibodies form in response to the neoantigen and bind to the surface of platelets, causing platelet aggregation, thrombocytopenia
Clinical signs
Suspected with heparin exposure >5 days and any of the following:
- Platelet count reduction >50% from baseline
- Arterial or venous thrombosis
- Necrotic skin lesions at heparin injection sites
- Acute systemic (anaphylactoid) reactions after heparin
Diagnostic
Serotonin release assay: Gold standard confirmatory test evaluation a Start treatment in suspected cases prior to confirmatory tests
Treatment
Stop ALL heparin products a Start a direct thrombin inhibitor (eg, argatroban) orfondaparinux (synthetic pentasaccharide)



